Archives
now browsing by author
Link Blogging by Tian’ao Wang
Tian’ao Wang’s linguistic blog
-
Language Change
The appearance of a new word marks only the beginning of its existence. Once generally adopted as part of the language, the meanings and applications it has for speakers can shift dramatically, to the point of causing misunderstandings. For example, “villain” once meant a peasant or farmhand, but has come to imply a criminal individual in modern English.Read more

-
Animal Communication
Language is a cognition that truly makes us human. Whereas other species do communicate with an innate ability to produce a limited number of meaningful vocalizations (e.g. bonobos), or even with partially learned systems (e.g. bird songs), there is no other species known to date that can express infinite ideas (sentences) with a limited set of symbols (speech sounds and words).Read more

-
-
Semantics
Syntax highlighting and indent style are often used to aid programmers in recognizing elements of source code. Color coded highlighting is used in this piece of code written in Python.Read more。

-
Linguistics
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search This article is about the field of study. For the journal, see Linguistics (journal). “Linguist” redirects here. For other uses, see Linguist (disambiguation) Read more

-
Indian Languages
Indigenous languages of the Americas are spoken by indigenous peoples from Alaska and Greenland to the southern tip of South America, encompassing the land masses that constitute the Americas. These indigenous languages consist of dozens of distinct language families, as well as many language isolates and unclassified languages.Read more
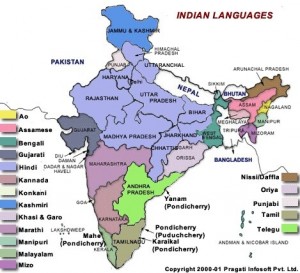
-
Language and Culture
The power of language to reflect culture and influence thinking was first proposed by an American linguist and anthropologist, Edward Sapir (1884–1939), and his student, Benjamin Whorf (1897–1941).Read more

-
-
Phonetics VS Phonology
Phonetics deals with the production of speech sounds by humans, often without prior knowledge of the language being spoken. Phonology is about patterns of sounds, especially different patterns of sounds in different languages, or within each language, different patterns of sounds in different positions in words etc.Read more

What is Morphology?
Webster’s New World Dictionary offers several most frequently used senses of the word”language”,namely,human speech;the ability to communicate by this means;a system of vocal sounds and combinations of such sounds to which meaning is attributed,used for the expression or communication of thought and feelings;the written representation of such a system;any means of expressing or communicating,as gestures,signs,or animal sounds;Read more
-

-
Language Acquisition
Semantics is een groep van gelijkgestemde individuen met een enorme passie voor talen, communicatie en coaching. Wij garanderen dynamische en begeesterende opleidingen met uitstekende resultaten, en putten hierbij uit een rijke pedagogische ervaring en business knowhow. Wij komen al uw behoeften tegemoet, helpen u uw doelstellingen te verwezenlijken en bouwen mee uw toekomst op.Read more
-
Syntax
Language storage and access studies how language is stored in our brain and how do we access it when we need it.The ability of human to speak and to understand speech requires an enormous amount of brain resources.Read more
-
Language Storage and Access
A recent advertisement for Lockheed products claimed that if William the Conqueror had not had technological superiority when he invaded England in 1066, “this very ad might have been written in Anglo-Saxon”. What’s wrong with this picture? Two things: First, all living languages are always changing, so the Old English spoken by William’s adversaries would be greatly different from Modern English even if there had been no Norman conquest.Read more
-
Language Variation
In linguistics, morphology is the identification, analysis, and description of the structure of a given language’s morphemes and other linguistic units, such as root words, affixes, parts of speech, intonations and stresses, or implied context. In contrast, morphological typology is the classification of languages according to their use of morphemes, while lexicology is the study of those words forming a language’s wordstock. Read more
-





 D5 Creation
D5 Creation